Understanding the Role of Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, muscle strength, and overall immunity. But what happens if I don’t get enough vitamin D? Deficiency is more common than most people realize, especially in regions with limited sun exposure or where dietary intake of fortified foods is low. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, and without it, bones can become brittle and weak.
Bone and Muscle Health – What Happens if I Don’t Get Enough Vitamin D?
One of the earliest effects of vitamin D deficiency is poor bone mineralization. In children, this condition is known as rickets, leading to soft and deformed bones. In adults, it can cause osteomalacia, resulting in bone pain and muscle weakness. The NIH and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) both confirm that long-term deficiency increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Furthermore, low vitamin D levels impair muscle function, raising the chances of falls, particularly in older adults.
Immunity and Chronic Diseases – What Happens if I Don’t Get Enough Vitamin D?
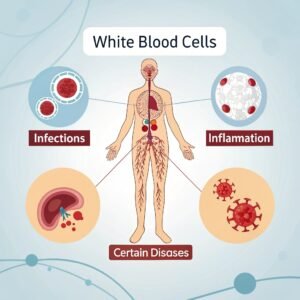
Beyond bone health, vitamin D supports immune function. Government-backed studies highlight that deficiency is linked with a higher susceptibility to infections like influenza and respiratory illnesses. Some research also suggests connections between low vitamin D and chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and even certain cancers, though evidence in these areas is still emerging. The Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS) notes that adequate vitamin D status may lower inflammation and strengthen the body’s defense system.
Healthcare Note:
Maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels is critical for long-term health. You can improve your status through safe sun exposure, vitamin D–rich foods such as fatty fish and fortified milk, or supplements if prescribed by a healthcare professional. A simple blood test can determine deficiency, and timely correction can prevent serious health complications.